Mind your Brain
Vascular dementia describes a wide range of symptoms associated with a decline in memory or other thinking skills severe enough to reduce a person’s ability to perform everyday activities.The after-effects can be minimized with early diagnosis and lifestyle changes
By Dr. K K Chaudhary
The word dementia describes a set of symptoms that can include memory loss and difficulties with thinking, problem-solving or language. In vascular dementia, these symptoms occur when the brain is damaged because of problems with the supply of blood to the brain. Vascular dementia may develop after a stroke blocks an artery in your brain, but strokes don’t always cause vascular dementia. Whether a stroke affects your thinking and reasoning depends on your stroke’s severity and location. Vascular dementia also can result from other conditions that damage blood vessels and reduce circulation, depriving your brain of vital oxygen and nutrients.
Causes
If the lumen of vessels within the brain becomes narrow gradually, it affects the blood supply to the brain and eventually brain cells are destroyed.
This death of brain cells can cause problems with memory, thinking or reasoning. Together these three elements are known as cognition. When these cognitive problems are bad enough to have a significant impact on daily life, this is known as vascular dementia.
Types of vascular dementia
There are several types of vascular dementia. They differ in the cause of the damage and the part of the brain that is affected. The different types of vascular dementia have some symptoms in common and some symptoms that differ. Their symptoms tend to progress in different ways.
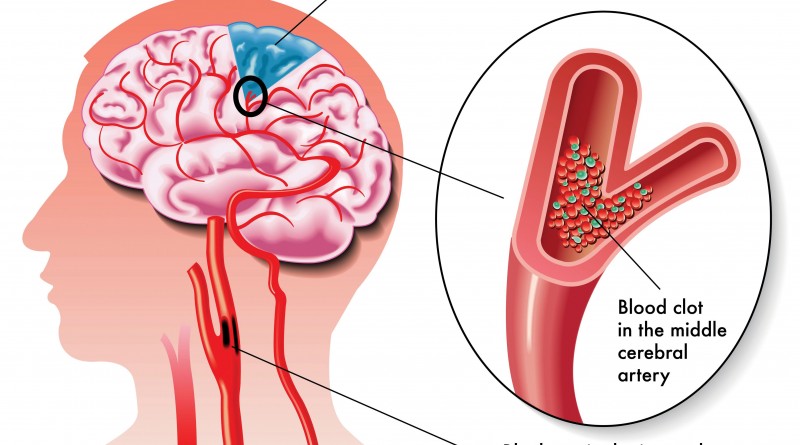
Stroke-related dementia: A stroke happens when the blood supply to a part of the brain is suddenly cut off. In most strokes, a blood vessel in the brain becomes narrowed and is blocked by a clot. This is called ischaemic stroke.
Do you Know?
About 20 per cent of people who have a stroke do develop this post-stroke dementia within the following six months.
Single-infarct and multi-infarct dementia: These types of vascular dementia are caused by one or more smaller strokes. These happen when a large or medium-sized blood vessel is blocked by a clot. The stroke may be so small that the person doesn’t notice any symptoms
Subcortical dementia: Subcortical vascular dementia is caused by diseases of the very small blood vessels that lie deep in the brain. These small vessels develop thick walls and become stiff and twisted, meaning that blood flow through them is reduced.
The most common cognitive symptoms in the early stages of vascular dementia are:
• Problems with planning or organizing, making decisions or solving problems
• Difficulties following a series of steps (eg cooking a meal)
• Slower speed of thought
• Problems concentrating, including short periods of sudden confusion.
A person in the early stages of vascular dementia may also have difficulties with:
• Memory – problems recalling recent events (often mild)
• Language – speech may become less fluent
• Visuospatial skills – problems perceiving objects in three dimensions.
Who can get affected by vascular dementia?
• Age is the strongest risk factor for vascular dementia. A person’s risk of developing the condition doubles approximately every five years over the age of 65. Vascular dementia under the age of 65 is uncommon. Men are at slightly higher risk of developing vascular dementia than women.
• A person who has had a stroke, or who has diabetes or heart disease, is approximately twice as likely to develop vascular dementia.
If someone does have dementia, an early diagnosis has many benefits: it provides an explanation for the person’s symptoms; it gives access to treatment, advice and support; and it allows them to prepare for the future and plan ahead. For vascular dementia, treatments and lifestyle changes may also slow down the progression of the underlying disease.
Blood thinning drugs like Ecosprin, helps in maintaining the blood flow of the brain.
(The author is Neurologist, Primus Super Speciality Hospital, New Delhi)