Mucormycosis Guidelines for Districts

Mucormycosis (Black Fungus) is a very rare infection. It is caused by exposure to mucor mould (a type of fungus) which is commonly found in soil, plants, manure, and decaying fruits and vegetables. It is found everywhere and found in soil and air and even in the nose and mucus of healthy people……
By Dr Deepti Sharma
It affects the sinuses, causing pan sinusitis. It can spread rapidly even overnightly to the eyes, brain, jaws and lungs and can be life-threatening in diabetic or severely immune- compromised individuals, such as cancer patients or people with HIV/AIDS & nowadays in patients on steroids for treating Covid infection.
It is believed that mucormycosis, which has an overall mortality rate of 50%, is being triggered by the use of steroids, a life-saving treatment for severe and critically ill Covid-19 patients. Steroids reduce inflammation in the lungs for Covid-19 and appear to help stop some of the damage that can happen when the body’s immune system goes into overdrive to fight off coronavirus. But they also reduce immunity and push up blood sugar levels grossly in both diabetics and non-diabetic Covid-19 patients. It’s thought that this drop in immunity could be resulting into mucormycosis. Diabetes lowers the body’s immune defences, coronavirus exacerbates it, and therefore control of Diabetes is very essential.
Predisposing Factors:
Uncontrolled Diabetes Mellitus
Immunosuppression by steroids
Treatment with Immunomodulators – Tocilizumab, Itolizumab, etc.
Prolonged ICU stay
Long standing oxygen therapy – specially by nasal prongs
Comorbidities – post-transplant, malignancies
Voriconazole therapy
Long term Ryles tube feeding
Humidifier bottle contamination
Prolonged use of higher antibiotics
Chronic Kidney Disease/ Chronic Liver Disease
 Prevention:
Prevention:
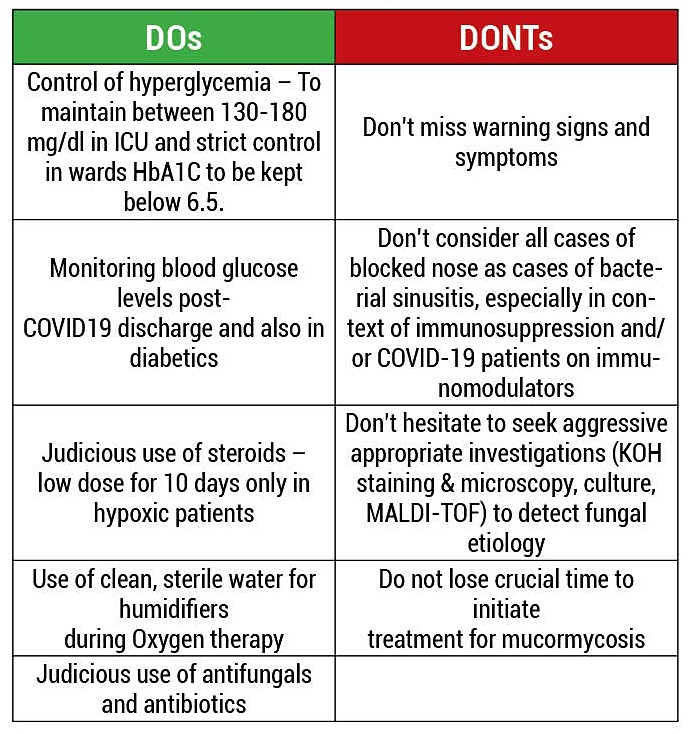
Strict glycemic control during management of COVID 19 patients is required.
Systemic steroids should only be used in patients with hypoxemia.
Oral steroids are contra indicated in patients with normal oxygen saturation on room air.
If systemic steroid is used, blood sugar should be monitored.
The dose and duration of steroid therapy should be limited to dexamethasone (0.1mg/kg/day) for 5-10 days.
Universal masking reduce exposure to Mucorales; avoidance of construction sites.
During discharge of the patients, advice about the early symptoms or signs of mucormycosis (facial pain, nasal blockage and excessive discharge, loosening of teeth etc., chest pain, respiratory insufficiency)
Strict infection control measures including cleaning & replacement of humidifier. Sterile normal saline should be used in the humidifier bottle & changed daily. Masks should be Disinfected daily.
Local Public Health Laboratory should be asked to take swabs of humidifiers, masks, tubings & common touch areas for culture of Mucormycosis.
Suspect:
(In COVID-19 patients, diabetics or immunosuppressed individuals)
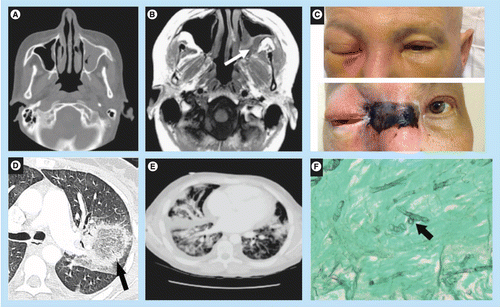
Sinusitis: nasal blockade or congestion, nasal discharge (blackish/bloody), local pain on cheek bone
One sided facial pain, numbness or swelling
Blackish discoloration over bridge of nose or palate
Toothache, loosening of teeth, jaw involvement, swollen gums
Blurred or double vision with pain; fever, skin lesion; ptosis; thrombosis and necrosis (eschar)
Loss of vision (early or late feature)
Chest pain, pleural effusion, hemoptysis, worsening of respiratory symptoms.
Seizures, stroke – in cases of cerebral involvement
Warning Signs and Symptoms:
Pain and redness around eyes and/or nose
Fever – usually mild
Epistaxis
Headache
Cough
Shortness of breath
Bloody vomiting
Altered mental status
Examination Findings:
Facial swelling
Facial discoloration
Ptosis
Proptosis
Restricted extraocular movements
Central Retinal Artery Occlusion
Ophthalmoplegia
Panophthalmitis
Palatal eschar
Nasal eschar
Investigations:
• Hemogram; Blood sugar levels – FBS, PPBS; HbA1C; RFT with Sr elctrolytes
• Deep nasal swab from Gram, KOH and Calcofluor White stain + plate blood agar and fungal media (SDA or PDA)
• Diagnostic nasal endoscopy; FESS.
• CT PNS; MRI Orbit, PNS and Brain with contrast.
• CT guided biopsy from ling for cultur / sensitivity.
• Bronchoscopic broncho-alveolar lavage for Histopathology.
Important points in management:
Infectious disease specialist, microbiologist, histopathologist, intensivist, neurologist, ENT specialist, ophthalmologist, dentist, surgeons, radiologists etc. have roles in the management.
Control of diabetes & diabetic ketoacidosis
Reduce steroids (if patient is still on) with aim to discontinue rapidly
Discontinue other immunomodulating drugs if patient is taking like: Baricitinib, Tofacitinib
Surgical debridement: Extensive, to remove all necrotic material; if eye involved, exenteration of eye; in pulmonary, if the lesion is localized or in one lobe.
Medical treatment
Surgical treatment.
Practical protocol to be followed:
Baseline HbA1c on Admission.
The strict control of blood sugar levels (110-180 mg/dl) and Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA).
Rational use of steroids in the high risk group.
Adequate humidification with distilled water used in the humidifiers of the Conventional /Low Flow / High Flow Oxygen delivery systems.
Isotonic-Saline Nasal Douche / Spray x 2 Times a day.
Maintain the Hygiene of Oxygen Delivery Systems.
Complete ENT Evaluation:
a) On Admission, DAY 1 & between Day 3 to 7 as per the clinical condition in the high-riskgroup.
b) At the Time of Discharge of a completely recovered COVID +ve, with the High-Riskfactors.
1. Diagnostic Nasal Endoscopy (DNE) + Otoscopy + Palatal Examination.
2. Deep Nasal Swab for KOH smear & Fungal Culture.
3. Biopsy (in Sterile Saline for Mycology & Formol Saline for Histopathology) at any point,in very high clinical suspicion – Day 1 till whenever and start liposomal amphotericin B (in very high clinical suspicion) without waiting for the Microbiology Reports.
Complete Ophthalmological Evaluation:
a) On Admission, DAY 1 and between Day 3 to 7 as per the clinical condition, in the high-risk group.
b) At the Time of Discharge of a completely recovered COVID + with High-Risk factors.
To examine the patient for early clinical signs of mucormycosis in the Anterior & Posterior Segment of the (Congestion / Chemosis / Pupillary Reaction / Motility / Central Retinal Artery Occlusion)
Criteria for examination by an ENT specialist & if required by an Opthalmologist on discharge. If the patient has had any of the following during admission:
Blood sugar level > 200
Hb1AC > 8
Oxygen therapy > 7 days
Steroid therapy > 7 days
Use of Tocilizumab
ICU stay > 7days
9. Radiological Evaluation:
Plain MRI PNS & Orbit to be done at any point, in very high clinical suspicion.
During the course of the Admission.
At the Time of Discharge of a completely recovered COVID + with very high clinicalsuspicion.
Advice to the Patient & Care Giver (At Discharge)
An educated & informed high-risk patient should be the protocol.Inform the patients about the early signs and symptoms of Mucor
Nasal Blockage
Blood tinged nasal discharge
Headache
Pain in the Eye
One sided Facial Pain & Swelling or Numbness
Toothache, Loosening teeth, discomfort during chewing
Swelling of the Eye & Adnexa
Double Vision
Note:
Immediately consult your treating Otorhinolaryngologist / Ophthalmologist, if you experience any of the aforementioned signs and symptoms.
Follow up on Day 7 and at 3 weeks.
Definition of High-Risk Group:
All COVID-19 cases with Uncontrolled DM + DKA / T2DM on Insulin with high dose Corticosteroids + Immunomodulators and require oxygen delivery systems.
Management:
(A) Medical management: Most important is to control blood sugar. While patient is on Ampho-B treatment, daily monitoring of RFT and Sr Electrolytes to check for hypokalemia is mandatory. Dose of Ampho-B needs to be titrated against GFR/ renal functions.
Amphotericin-B (crystalline) should be preferred. Only if the patient has deranged RFTs / LFTs or the patient does not tolerate, then Amhotericin-B (Liposomal or Lipid) should be used.
Induction with Liposomal Amphotericin-B (L-AMB): 5-10 mg/kg/day for 2 weeks [All patients] OR Deoxycholate formulation of Amphotericin-B: 0.7 – 1.0 mg/kg daily (this is more toxic)
Dual therapy: L-AMB + Oral Posaconazole (300 mg BD on Day 1 f/b 300 mg OD for 2 weeks) [All patients]
Oral Posaconazole 300 mg BD for a further 2-4 weeks till clinical resolution and radiological stabilization. [All patients]
Monitor patients clinically, with radio-imaging for response / disease progression & microbiologically
After 3-6 weeks of amphotericin B therapy, consolidation therapy (posaconazole/isavuconazole) for 3-6 months
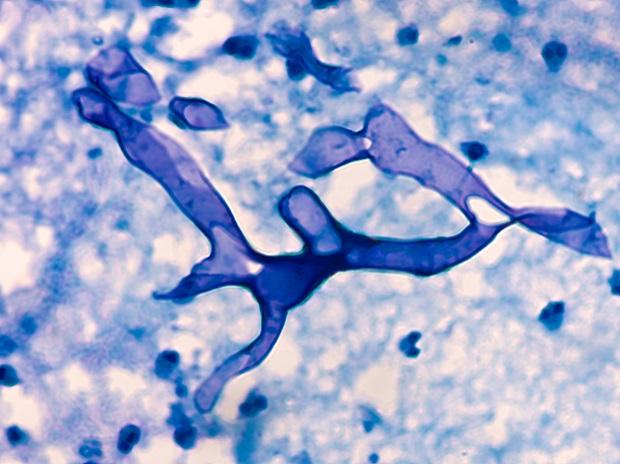
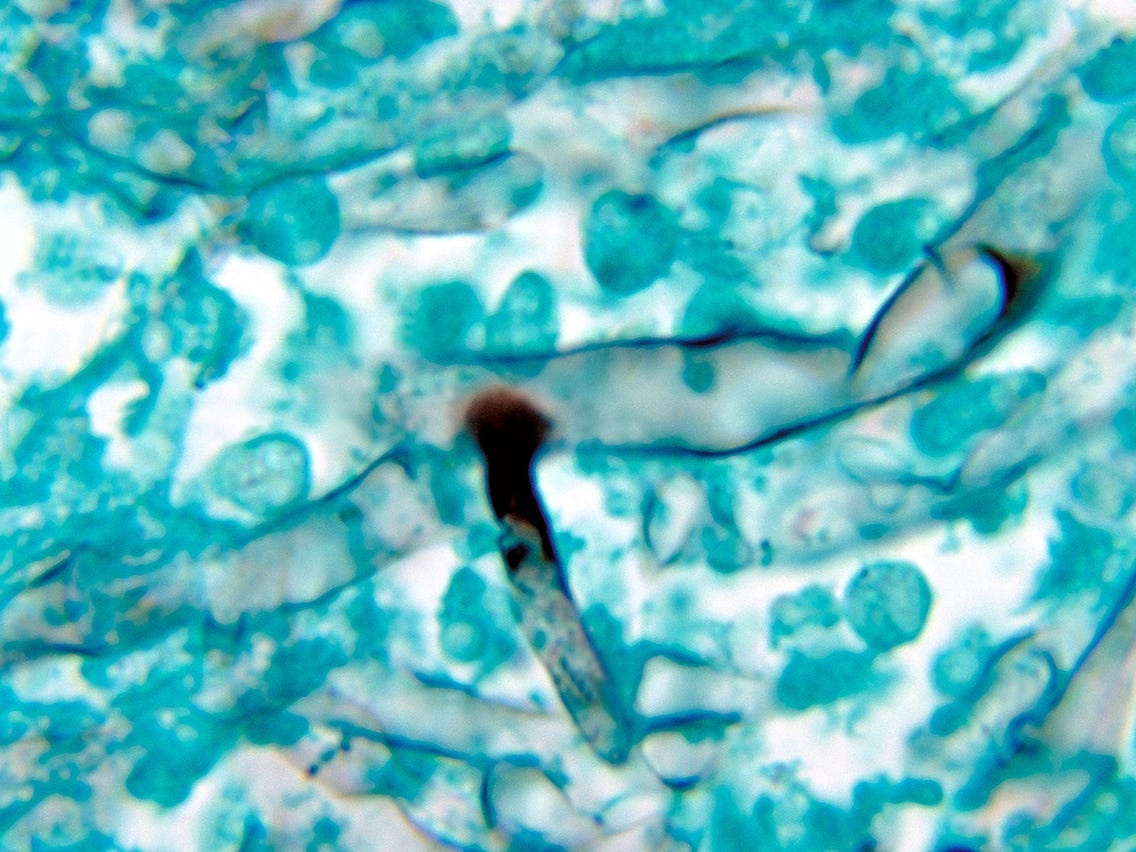
(B) Surgical management: After dressing of Mucormycosis patient, gloves should be changed before touching another patient to avoid contact transmission of mucor to other patient.
Early surgical debridement of sinuses [All patients]
Transcutaneous Retrobulbar Amphotericin B (TRAMB): 1 ml of 3.5 mg/ml [Select cases only]
Orbital Exenteration:
For patients with extensive orbital involvement.
In follow-up of this patient, recurrence should be closely monitored for. Strict long term diabetic control is needed for the same
As surgical treatment involves disfigurement of face, consultation of a plastic surgeon can be sought.
Guidelines for the system of reporting the data of Mucormycosis is given separately.
The Author is Fellow Forensic Odontology, Cert (WMD), Cert
(Implants) General Secretary For Council Of Accredited Forensic Odontologist approved by Govt Of India Owner / Director
Dr Sharma Dental Care.