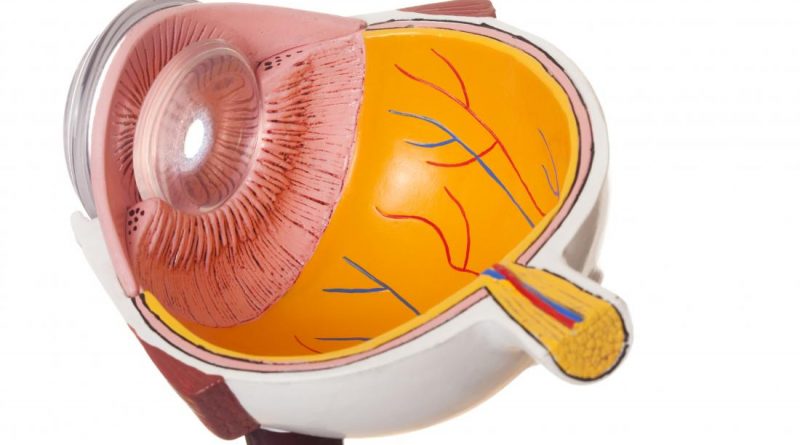
Central Serous Retinopathy

Central serous retinopathy (CSR) is an idiopathic disease which affects the central area of retina known as the macula. It primarily affects at age group of, 20 to 50 years of age, although it is seen occasionally in older patients, females, and other ethnic groups….…
By Dr Shishir Narayan
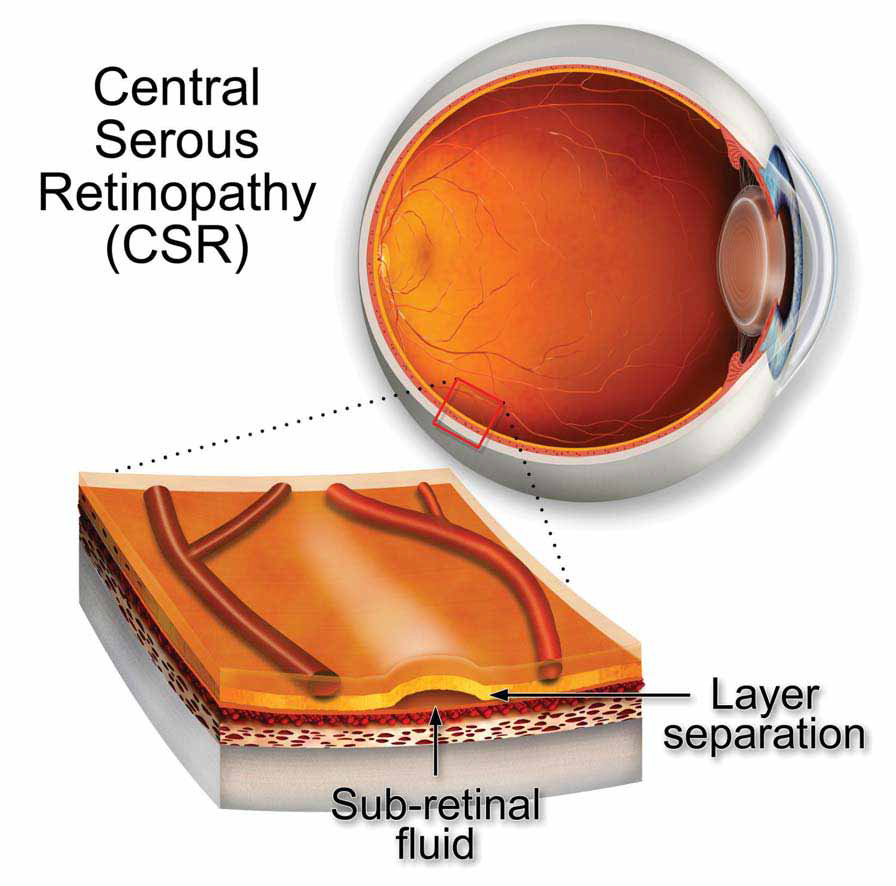
Today the Stress is a major risk factor. People under a lot of stress may be more likely to develop central serous retinopathy. The CSR can cause vision to be blurred and distorted due to fluid collecting underneath the macula. In most people, CSR gets better on its own and doesn’t cause long-term changes to vision. In some people it may re-occur. Episodes of CSR that last for a long time or keep coming back are more likely to cause permanent changes in vision.
The condition may be triggered or exacerbated by stress or corticosteroid use. The retina is responsible for translating light taken into the eye as images the brain can understand. The build-up of liquid can cause the retina to detach, and this can cause vision problems.
 Symptoms
Symptoms
Blurry vision is a common symptom. A person may also notice that the area around their central vision starts to darken or becomes blurry. In most cases, the vision issue is limited to one eye. It is possible that a person may develop the condition in each eye at separate points throughout their life.
Additional symptoms of central serous retinopathy may include: objects appear farther away, whites may appear duller, and lines appear crooked and a dark spot in the center of vision. Central serous retinopathy does not always produce symptoms. It is possible that fluid may build up in areas that are not around the macula, which is responsible for clear central vision. If this happens, a person may have the condition without knowing it because they do not have any symptoms.
How affect vision?
The swelling in the macula can cause blurry vision, distortion, blind spots, muted colours and objects appearing smaller than they are. One may also have trouble with bright light and your ability to see an object against a background of similar colour (contrast sensitivity) could be reduced. Some people may find that their vision fluctuates – on some days they may see better and other days not very well at all. For some people, the swelling may not cause any visual symptoms at all.
 What causes CSR?
What causes CSR?
In most cases of CSR, the cause is unknown while it is idiopathic, which means no cause can be found to explain why it occurred. However, several possible risk factors have been identified. The condition seems to occur more frequently in people:
with a Type A personality (people who are stressed and find it hard to relax)
- who use steroid medication
- during pregnancy
- With Cushing syndrome.
Generally speaking, the way CSR may progress can be grouped into three categories. Most people will recover within 4-6 months without any need for treatment. CSR may lasts up to 12 months depending on regular treatment and precautions. This is very rare but can lead to further changes such as RPE detachment or bullous retinal detachment. In a small number of people, CSR can be chronic, lasting longer than 12 months. In these cases, sight is more at risk because the retinal layers at the back of your eye can become damaged from prolonged swelling.
How is CSR treated?
Most people with CSR don’t require treatment. If treatment is required then thermal laser or photodynamic therapy (PDT) may be used. When deciding on treatment, the ophthalmologist (hospital eye doctor) would consider:
- How long you have had CSR, as treatment would only be considered after 4-6 months of the initial diagnosis.
- If you experience a recurrence, then treatment may be considered sooner.
- Thermal laser treatment is not given if the fluid is leaking too close to the centre of the macula because it could cause more harm than good.

Yellow micropulse laser appears to be effective for chronic CSR. No retinal damage was seen in any of the eyes, except for minimal hyper fluorescence in one immune compromised patient with RPE changes in both eyes prior to treatment. While most patients responded well within 30 days of treatment, some may need more than one laser treatment. Long-term, prospective studies are needed to confirm the safety and efficacy of this approach. Sometimes another type of treatment called photodynamic therapy is more suitable for people who are at risk of scarring on their macula that could permanently damage their vision. Photodynamic therapy combines laser treatment with a light-sensitive drug to treat the condition.
Fast Facts
The retina is responsible for translating light taken into the eye as images the brain can understand. The build-up of liquid can cause the retina to detach, and this can cause vision problems. In some cases, no medical intervention is required, and the person will recover their vision after a short period. However, people should see their doctor immediately if they start to notice changes in vision.
Mostly it is still unknown the exact causes of central serous retinopathy, but the some factors may contribute to its development like Stress which is a likely cause of central serous retinopathy. Stress causes the body to produce a hormone called cortisol. In the early stages, a person is likely to notice blurry vision. In some cases, a person may not experience any changes in vision. The fluid that builds behind the eye may drain away on its own.
What to do
There are some general lifestyle changes a person can make. Some changes include reducing overall stress levels, such as through exercise, sleeping for at least seven hours each night, avoiding alcoholic drinks and reducing caffeine intake.
(The author is senior Eye Specialist, Asia Colombia Hospital and associated with Shroff Eye Hospital, New Delhi)