Music Therapy for Health and Wellness
 Today music therapy has proved as positive effects on stress, pain management, mood regulation, cognitive function, and overall quality of life…….
Today music therapy has proved as positive effects on stress, pain management, mood regulation, cognitive function, and overall quality of life…….
By Dr. Chandrakant S. Pandav/ Rishi S. Bharadwaj
With advent of non-invasive, evidence-based intervention music therapy has gained attention in recent years as a complementary treatment option for a wide range of physical, emotional, and cognitive health issues. The review examines the current state of knowledge regarding music therapy’s effectiveness in promoting health and wellness, the mechanisms underlying its therapeutic effects, and its potential as an integrative approach to care.
According to research, the role of music therapy is promoting health and wellness. Music has been used for therapeutic purposes since ancient times, with evidence of its use dating back to the Samveda in India. Shiva’s Damru is considered the first musical instrument and highlights the significance of music in ancient cultures.
Shiva’s Damru–The First Musical Instrument
According to Hindu mythology, Shiva’s Damru is believed to be the first musical instrument. It is said that when Shiva played the Damru, it created a sound that encompassed all aspects of creation – from the highest vibrations of the cosmos to the lowest vibrations of the earth. The Damru is made of a small drum with two sides, and it is played by shaking the drum back and forth while holding it with a string.

The sound of the Damru is considered to be extremely powerful and is believed to have the ability to create and destroy entire universes. It is also said to be a symbol of the heartbeat of the cosmos and the rhythm of life itself. In Hindu tradition, the Damru is often depicted as being held by Nataraja, a form of Shiva that represents the cosmic dance of creation and destruction.
In modern times, the Damru is still used in traditional Indian music, particularly in devotional music and bhajans. It is also sometimes used in meditation and yoga practices, as the sound of the Damru is believed to help facilitate deep relaxation and spiritual awakening.
Overall, the Damru is an important symbol in Hindu mythology and is considered to be the first musical instrument, with a powerful sound that represents the rhythm of the cosmos and the cycle of life and death.
 Reference to Music in the Samveda
Reference to Music in the Samveda
The Samveda, an ancient Indian text, is one of the four Vedas that are considered the most sacred and revered texts of Hinduism. It is believed to have been compiled around 1000-500 BCE and is dedicated to the importance of music and its role in promoting spiritual and physical wellbeing.
The Samveda contains numerous references to the healing power of music, highlighting its ability to calm the mind and soothe the soul. The text describes music as a divine language that has the power to connect individuals with the divine, allowing them to experience a state of peace and tranquility.
In the Samveda, the use of music for therapeutic purposes is known as Gandharva Veda. Gandharva Veda was believed to be a branch of Ayurveda, the traditional Indian system of medicine. It was considered an essential tool in the healing process and was used to treat a range of physical and mental ailments.
The Samveda contains detailed descriptions of the various instruments used in Gandharva Veda, including the vina, the flute, and the mridangam. It also includes descriptions of the different ragas or musical modes and their specific therapeutic effects. For example, the raga Bhairavi was believed to have a calming effect and was often used to treat anxiety and insomnia.
The concept of Nada Brahma, which means “sound is God” or “sound is the divine”, is another important aspect of the Samveda. According to this concept, sound is considered a manifestation of the divine and has the power to connect individuals with the divine. It was believed that through the use of music, individuals could reach a state of transcendence and experience a deep sense of inner peace and harmony.
Today, the healing power of music is still recognized in India, with the practice of music therapy being used to treat a range of physical and mental health conditions. The influence of the Samveda can still be seen in modern Indian music therapy practices, with many of the therapeutic techniques and principles being derived from the ancient text.
In conclusion, the Samveda is a testament to the long-standing belief in the healing power of music. Its teachings continue to influence modern music therapy practices, highlighting the enduring significance of this ancient text in promoting physical and spiritual wellbeing.
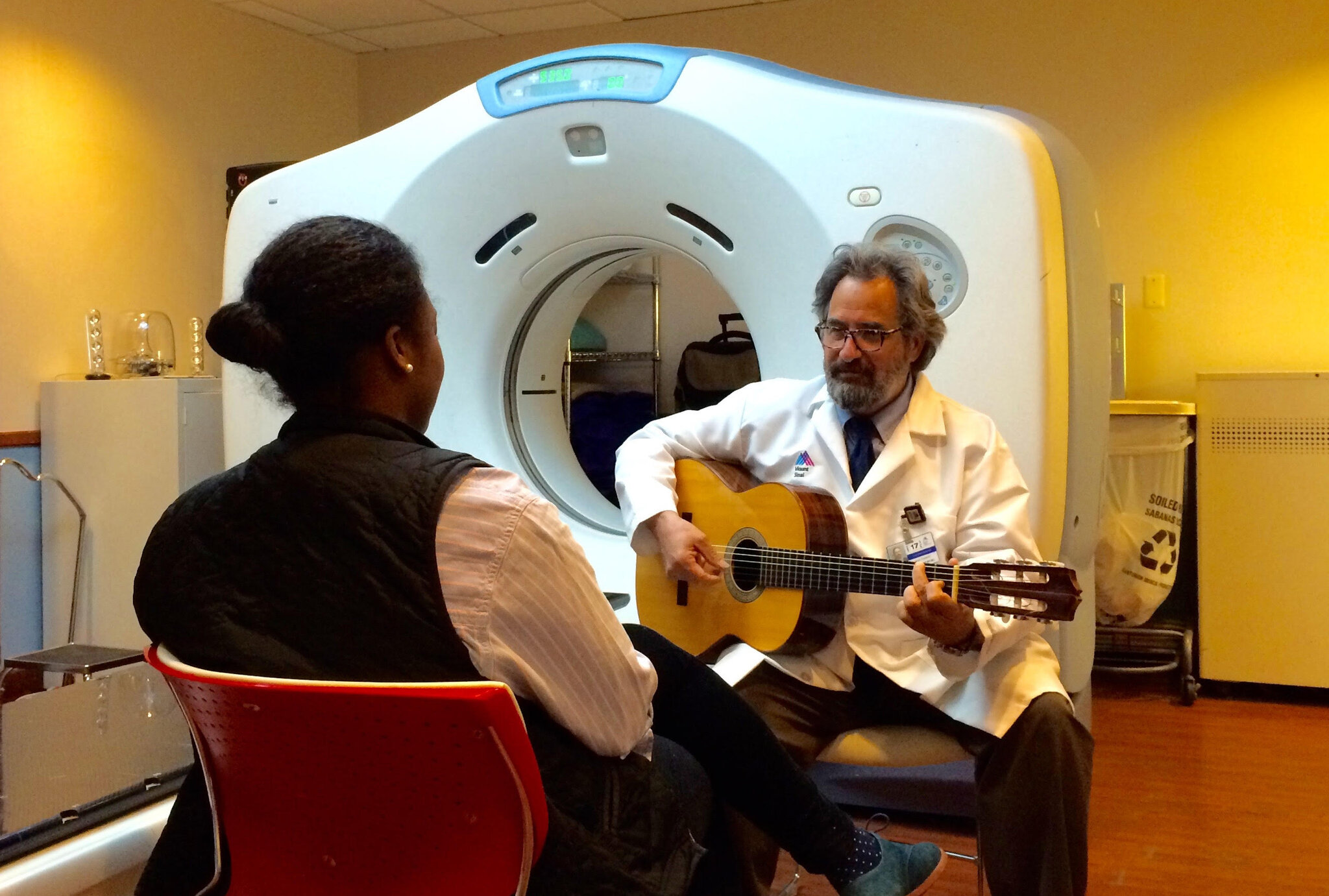 Ragas promoting health and wellbeing in Music Therapy
Ragas promoting health and wellbeing in Music Therapy
There are several ragas or musical modes that have been shown to be effective in music therapy for promoting health and wellbeing. Each raga is believed to have a specific therapeutic effect on the mind and body, and can be used to treat a range of physical and mental health conditions.
For example, the raga Yaman is known for its ability to calm the mind and reduce anxiety. It is often used in music therapy to treat conditions such as insomnia and depression. The raga Bhairavi is another popular raga used in music therapy, known for its ability to promote relaxation and reduce stress.
The raga Todi is believed to have a rejuvenating effect on the body and mind, and is often used to treat conditions such as fatigue and chronic pain. The raga Darbari is believed to have a meditative effect and is used to promote a sense of inner peace and tranquility.
Other ragas commonly used in music therapy include Shree, Malkauns, and Bageshree. Each raga is believed to have its own unique therapeutic effect and can be tailored to the individual needs of the patient.
The therapeutic effects of these ragas are believed to be due to the specific combination of notes and rhythms used in each raga. The notes and rhythms are thought to stimulate specific areas of the brain, promoting the release of certain neurotransmitters and hormones that can influence mood, behavior, and physiological processes.
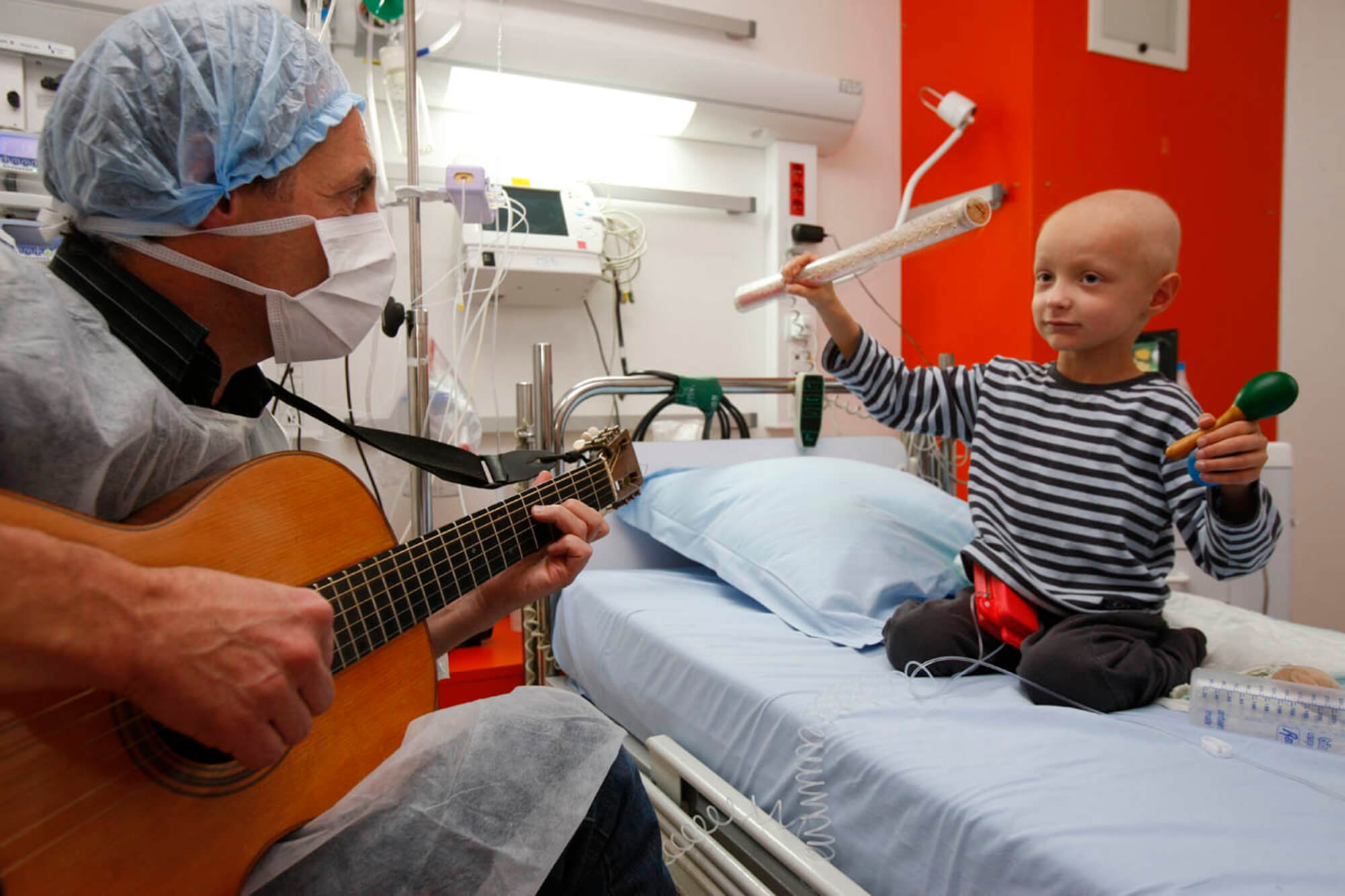 Overall, the use of specific ragas in music therapy is an important aspect of the practice and highlights the importance of tailoring therapy to the individual needs of each patient. By harnessing the therapeutic power of music, music therapists can provide a safe, non-invasive, and effective treatment option for a range of physical and mental health conditions.
Overall, the use of specific ragas in music therapy is an important aspect of the practice and highlights the importance of tailoring therapy to the individual needs of each patient. By harnessing the therapeutic power of music, music therapists can provide a safe, non-invasive, and effective treatment option for a range of physical and mental health conditions.
This article also highlights some of the challenges facing the field, including the need for standardized protocols, increased research funding, and greater recognition from healthcare providers. Overall, the evidence suggests that music therapy has the potential to be a valuable addition to conventional healthcare practices, offering a safe, low-cost, and accessible intervention for individuals seeking to optimize their health and well-being.
Several studies have demonstrated that music therapy can reduce stress and anxiety levels in both healthy individuals and those with chronic illnesses such as cancer and cardiovascular disease. Music therapy has also been shown to be an effective adjunct to pain management, particularly for postoperative pain and chronic pain conditions such as fibromyalgia and osteoarthritis. The studies have also reported improvements in mood and emotional regulation following music therapy interventions, particularly in individuals with depression, anxiety, and dementia. Additionally, music therapy has been found to enhance cognitive function, particularly in domains such as attention, memory, and executive function. Finally, music therapy has been shown to have a positive impact on overall quality of life, including social functioning, self-esteem, and sense of purpose
Music has been a source of comfort, solace, and inspiration for humans throughout history, but it is only in recent years that its potential as a therapeutic tool has been fully recognized. Music therapy is a clinical and evidence-based approach that utilizes music to address physical, emotional, cognitive, and social needs. It is a form of complementary medicine that can be used in conjunction with traditional medical interventions to enhance the overall well-being of patients. Music therapy can be applied in a variety of settings, including hospitals, nursing homes, rehabilitation centers, and private practices, and it has been shown to be effective in treating a range of health conditions. In this review, we explore the scientific evidence behind music therapy’s therapeutic effects, the mechanisms by which it works, and its potential as a complementary approach to healthcare.
Music has been found to have a profound impact on human beings, both physiologically and psychologically. The effects of music on the brain and body are complex and can vary depending on factors such as the type of music, the individual’s personal preferences and experiences, and the context in which the music is experienced.
At a physiological level, music has been shown to affect heart rate, blood pressure, and respiration. It can also trigger the release of hormones such as cortisol and oxytocin, which can have both positive and negative effects on mood and stress levels. For example, slow, calming music has been found to reduce stress and lower heart rate and blood pressure, while faster, more upbeat music can increase heart rate and arousal.
In addition to its physiological effects, music has also been found to have powerful psychological effects. It can evoke a range of emotions, from joy and excitement to sadness and melancholy, and can facilitate emotional expression and regulation. This is thought to be due in part to the way music activates multiple areas of the brain, including regions involved in emotional processing, memory, and attention.
Music has also been shown to have cognitive benefits, such as enhancing attention and memory. This is thought to be due to the way music engages the brain’s neural networks, promoting the formation and strengthening of connections between brain regions.
When used in a therapeutic context, music can be a powerful tool for promoting health and wellbeing. Music therapy can be used to help manage symptoms of a range of health conditions, from anxiety and depression to chronic pain and neurological disorders.
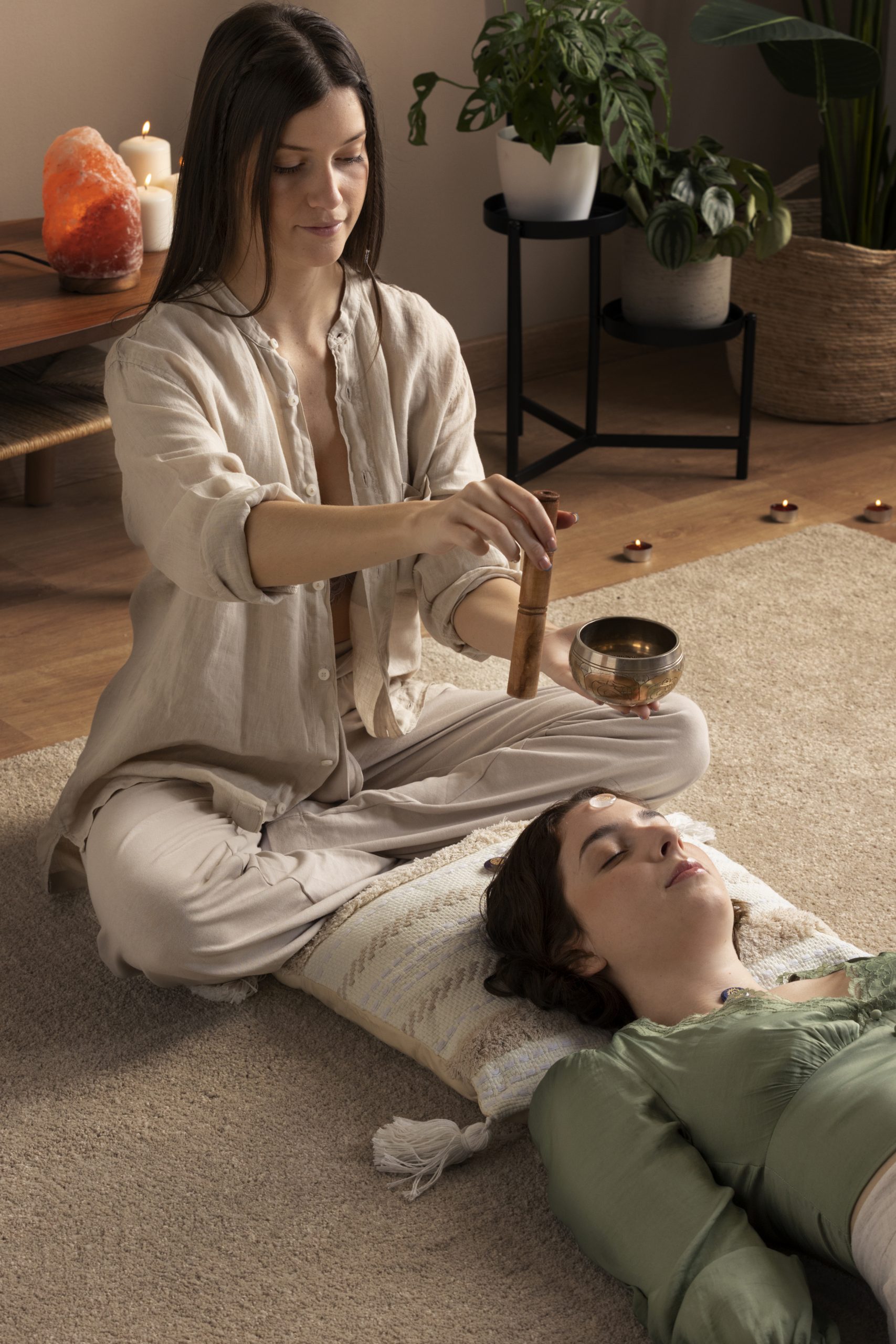 Overall, the effects of music on human beings are complex and multifaceted, with both physiological and psychological dimensions. While the mechanisms underlying these effects are still not fully understood, the growing body of research on the subject suggests that music can be a valuable tool for promoting health and wellbeing.
Overall, the effects of music on human beings are complex and multifaceted, with both physiological and psychological dimensions. While the mechanisms underlying these effects are still not fully understood, the growing body of research on the subject suggests that music can be a valuable tool for promoting health and wellbeing.
The exact mechanisms underlying music therapy’s therapeutic effects are not yet fully understood, but several theories have been proposed. One theory suggests that music activates the same reward pathways in the brain as other pleasurable experiences, such as food and sex, leading to the release of dopamine and other neurotransmitters associated with pleasure and reward. Another theory suggests that music can modulate the autonomic nervous system, leading to changes in heart rate, blood pressure, and other physiological parameters. Additionally, music therapy may facilitate emotional expression and regulation, which can promote healing and reduce stress. It may also enhance cognitive processes such as attention and memory by engaging multiple areas of the brain.
Despite the growing body of evidence supporting the use of music therapy as a complementary approach to healthcare, the field still faces several challenges. One of the major challenges is the lack of standardized protocols for music therapy interventions. While there is some consensus on basic principles of music therapy, such as the importance of individualization and the use of live music, there is still significant variation in the way music therapy is practiced across different settings and practitioners. This variability can make it difficult to compare results across studies and may limit the broader adoption of music therapy as a treatment option.
Another challenge facing the field is the need for more research funding. While there have been several high-quality studies demonstrating the effectiveness of music therapy, more research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms underlying its therapeutic effects and to identify the most effective interventions for specific health conditions. Funding for music therapy research is often limited, however, due to a lack of awareness and understanding of the field among funding agencies.
Finally, there is a need for greater recognition of music therapy among healthcare providers. While many healthcare professionals are aware of music therapy, it is still not widely integrated into conventional healthcare practices. This may be due in part to a lack of understanding of the evidence supporting its effectiveness, as well as a lack of standardized training programs for music therapists.
Music therapy is a promising complementary approach to healthcare that has been shown to have positive effects on a range of health outcomes. While the field still faces several challenges, including the need for standardized protocols, increased research funding, and greater recognition among healthcare providers, the evidence suggests that music therapy has the potential to be a valuable addition to conventional healthcare practices. Future research should focus on identifying the most effective music therapy interventions for specific health conditions and on further elucidating the mechanisms underlying its therapeutic effects.
(The authors are Padmashree Awardee (2021), Former Professor & Head, Centre for Community Medicine, AIIMS, New Delhi/ Adjunct Professor, Symbiosis Skills and Professional University, Pune)

